The United States Supreme Court has seen a distinguished lineage of justices who have played pivotal roles in shaping the nation’s legal landscape. Throughout history, certain justices have left an indelible mark on American jurisprudence, setting precedents, interpreting the Constitution, and influencing the direction of the law.

These are some of the names and legacies of the most influential Supreme Court justices.
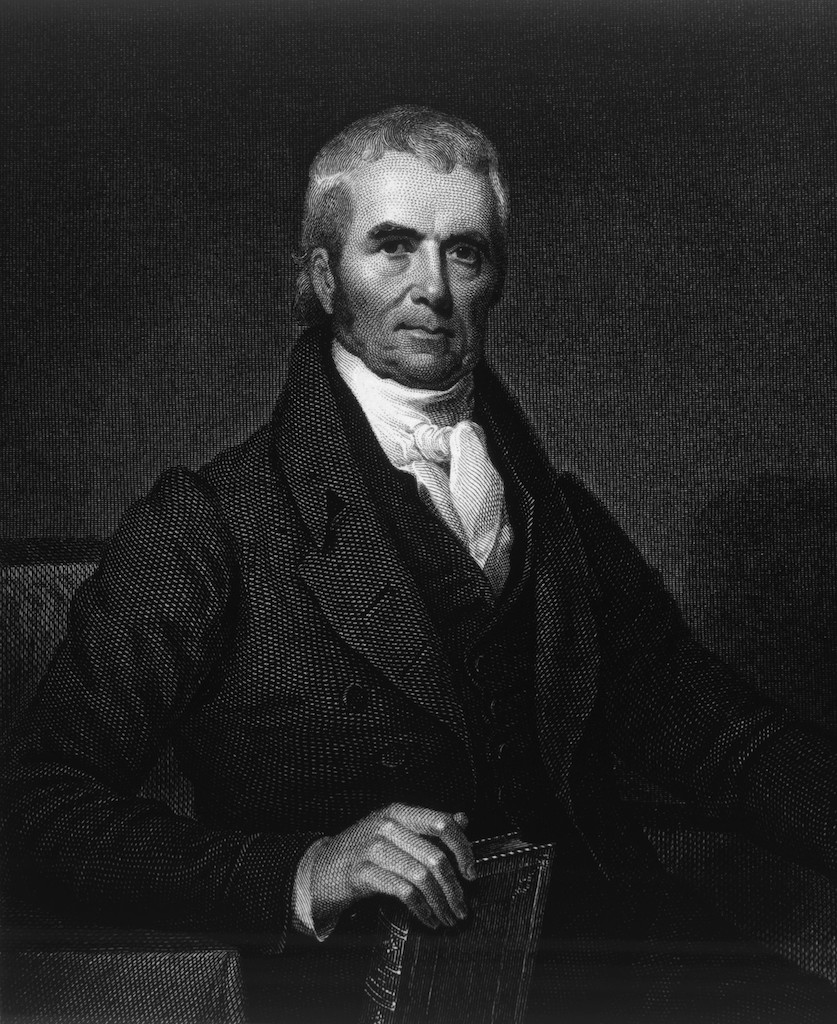

John Marshall (1801-1835)
John Marshall, the fourth Chief Justice of the United States, is widely regarded as one of the most influential justices in American history. Marshall’s tenure was marked by his expertise in constitutional interpretation and the establishment of the Court’s power of judicial review in the landmark case of Marbury v. Madison (1803). His decisions, such as McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) and Gibbons v. Ogden (1824), expanded federal power and laid the foundation for a robust and centralized national government.
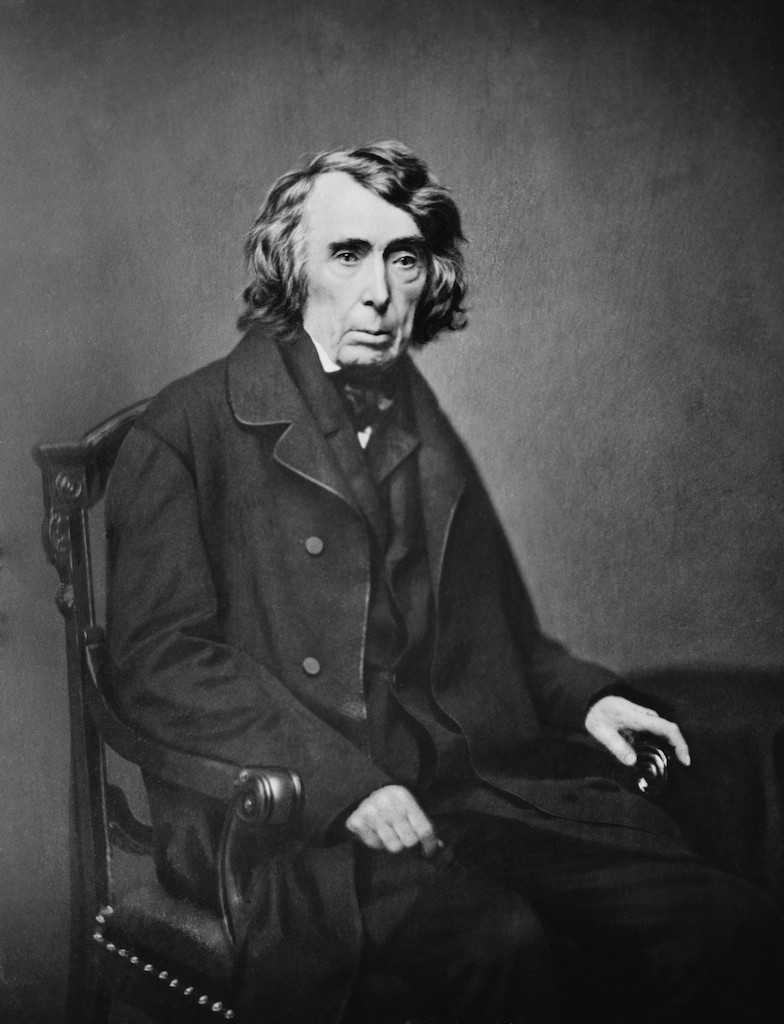

Roger B. Taney (1836-1864)
Roger B. Taney, the fifth Chief Justice, is often remembered for his controversial opinion in Dred Scott v. Sandford (1857), which declared that African Americans, whether free or enslaved, were not entitled to U.S. citizenship. While this decision remains a stain on his legacy, Taney’s influence extended beyond this case. He presided over the Court during a time of significant social and political upheaval, addressing issues such as states’ rights, slavery, and the expansion of federal power.
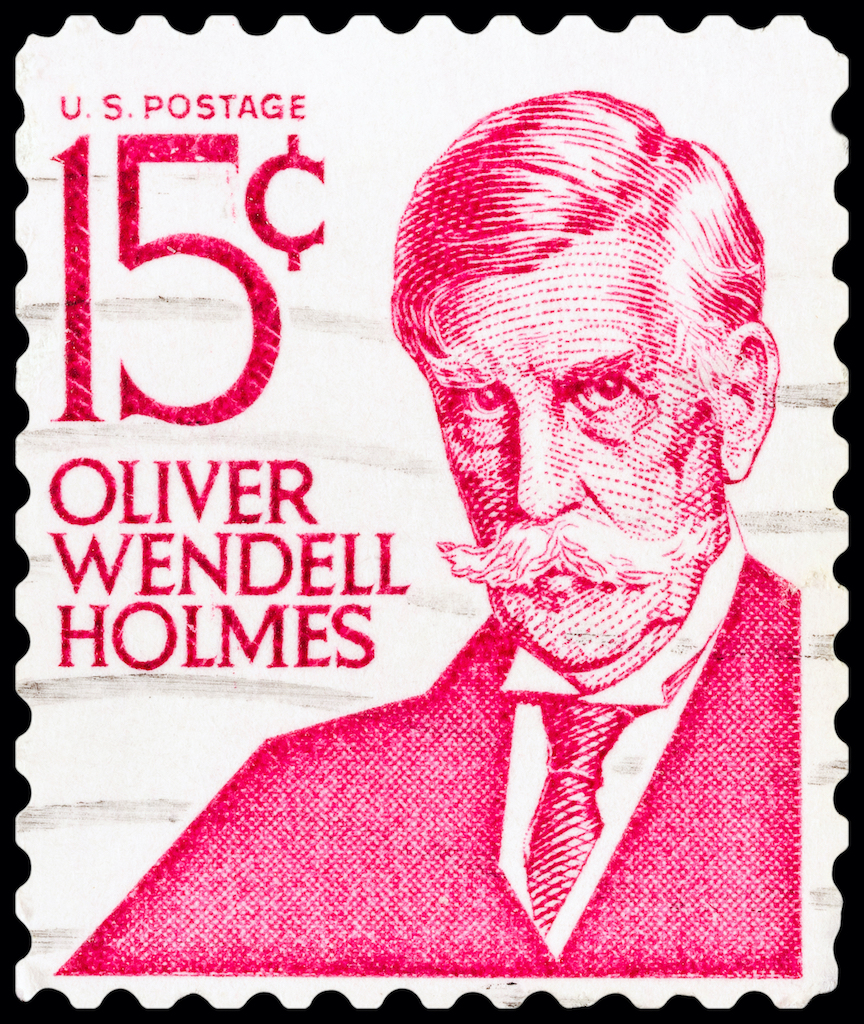

Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. (1902-1932)
Oliver Wendell Holmes Jr. is renowned for his profound impact on American legal thought. As an associate justice, Holmes championed the idea that the law must evolve to meet the changing needs of society. His famous dissent in Lochner v. New York (1905) challenged the Court’s embrace of substantive due process and advocated for judicial deference to legislatures. Holmes’s jurisprudential philosophy, emphasizing the importance of societal context, significantly influenced later generations of legal thinkers.
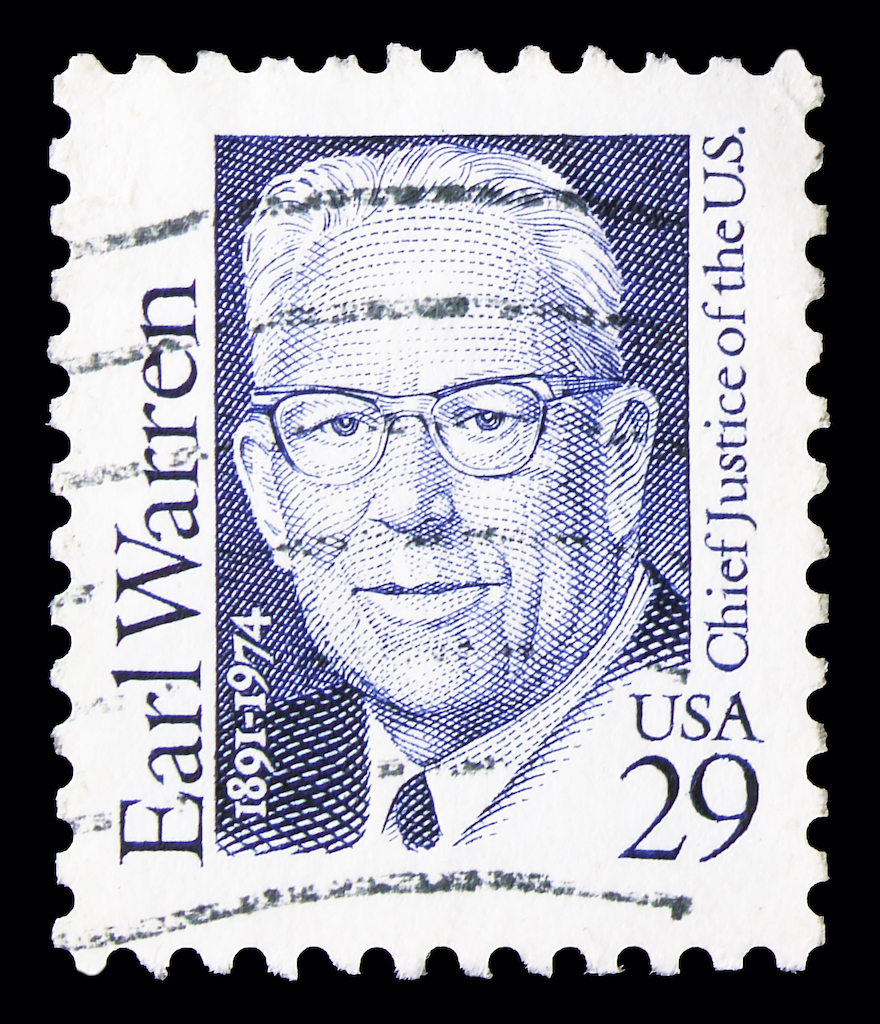

Earl Warren (1953-1969)
Earl Warren served as the 14th Chief Justice and presided over the Warren Court, a period marked by groundbreaking decisions that reshaped American society. Under Warren’s leadership, the Court handed down landmark rulings in Brown v. Board of Education (1954), which desegregated public schools, and Miranda v. Arizona (1966), which established the rights of the accused during police interrogations. Warren’s Court expanded civil liberties, protected individual rights, and advanced the cause of racial equality.

Thurgood Marshall (1967-1991)
Thurgood Marshall, the first African American Supreme Court justice, dedicated his career to fighting for civil rights and equality. As an attorney for the NAACP, Marshall successfully argued Brown v. Board of Education before the Court, leading to the end of racial segregation in public schools. Throughout his tenure on the bench, Marshall remained a staunch advocate for individual rights, emphasizing equal protection under the law and fighting against racial discrimination.