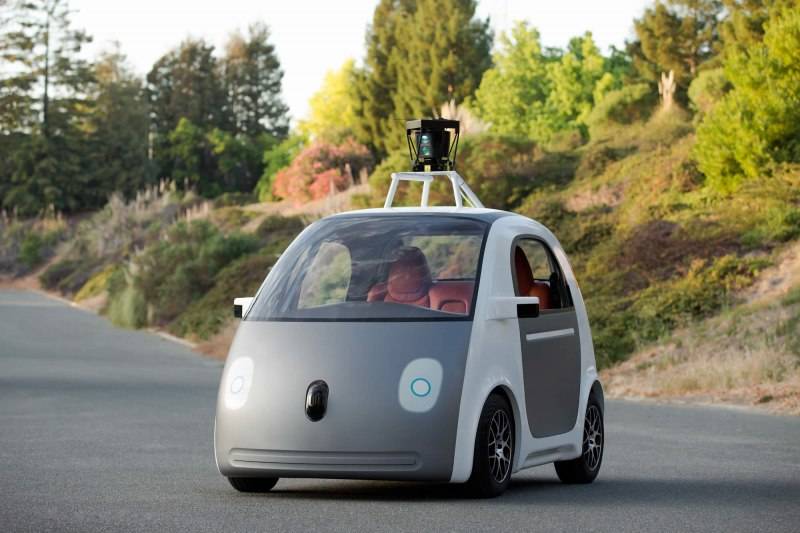
Haute 100: Google’s Self-Driving Car Cleared By NHTSA
As Google inches closer to debuting its autonomous car, The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) has issued an update to its vehicle safety regulation. In a letter posted on NHTSA site, the agency says the self-driving car can be considered a driver under federal law.
Last November,Chris Urmson, the director of Google’s self-driving car project, submitted a proposed design for a self-driving car that has “no need for a human driver.” Since reviewing Google’s proposal, the agency has sided with the silicon tech company.
“NHTSA will interpret ‘driver’ in the context of Google’s described motor vehicle design as referring to the (self-driving system), and not to any of the vehicle occupants,” NHTSA’s letter said. “We agree with Google its (self-driving car) will not have a ‘driver’ in the traditional sense that vehicles have had drivers during the last more than one hundred years.”
Thus far the company has tested more than one million miles and are currently out on the streets of Mountain View, CA, Austin, TX and Kirkland, WA. The company is testing fleet includes both modified Lexus SUVs and new prototype vehicles that are designed from the ground up to be fully self-driving. Currently, there are safety drivers aboard all vehicles, for now.
The autonomous car features sensors designed to detect objects as far as two football fields away in all directions, including pedestrians, cyclists and vehicles—or even fluttering plastic shopping bags and rogue birds. It also boasts electric batteries to power the vehicle on and off as well as back-up systems for sterring, braking, computing, etc. According to Google, the software processes all the information to help the car safely navigate the road without getting tired or distracted.
Google has been working on the project since 2009.
Other companies working on a autonomous car includes Mercedes-Benz, Apple, Tesla, to name a few.
Photo via Google