Dr. Melissa Toyos is an oculofacial surgeon specializing in FUE (follicular unit extraction) hair and eyebrow transplantation, CO2 facial resurfacing, and sculpting faces with injectables. A summa cum laude graduate and board-certified Ophthalmologist, she is a partner at Toyos Clinic and formerly was a partner at one of the largest eye care practices in the country. Dr. Toyos is a national researcher and lecturer. She trains other doctors on surgical techniques as well as cosmetic procedures. Her clinical research has been instrumental in many FDA approvals. She is the former President of the Missouri Society of Eye Physicians and Surgeons. She has held various leadership positions with the AAO. Dr. Toyos has served as a mentor to young female surgeons, helping them understand how to balance a career and motherhood.
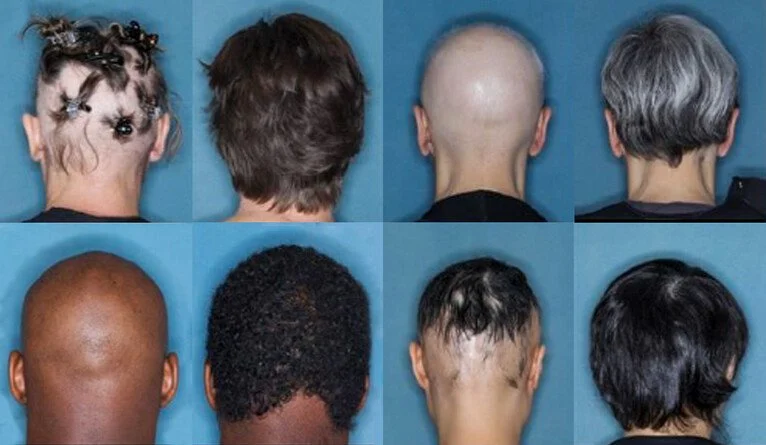 Photo Credit: Brett King Yale University
Photo Credit: Brett King Yale University
If you are suffering from alopecia areata, an autoimmune condition that causes the body’s own hair follicles to fall out, Haute Beauty expert Dr. Melissa Toyos finally has some great news for you! Meet OLUMIANT the first-in-class treatment approved for alopecia areata. To learn more about how the treatment can work for you, Dr. Toyos sat down with Haute Beauty to share all the details. Here’s what was learned:
What are the side effects of alopecia areata?
Alopecia areata can cause patchy or even total hair loss on the scalp, brows, beards and eyelashes. Most patients notice a round or oval bald patch on the scalp. They are often so defined that they look like a crop circle of hair loss but can also present with more diffuse hair loss.
How can alopecia areata be treated?
Before OLUMIANT, alopecia was treated with steroids injected or topically applied to the areas of hair loss, PRP, topical prostaglandins like Latisse, or minoxidil. Medications that help downregulate the overactive immune system like steroids, methotrexate, and JAK inhibitors have also been used in tough cases, especially when patients suffer other autoimmune conditions like psoriasis.
JAK or Janus kinase inhibitors work by blocking a messaging pathway that is triggered when specific inflammatory molecules bind to receptors on immune cells. Instead of allowing the cascade of inflammation to continue and amplify, JAK inhibitors inhibit a family of enzymes that slow down or block the inflammatory pathway.
JAK inhibitors are currently in use for autoimmune diseases and especially for rheumatoid arthritis. But on June 13, the FDA approved one JAK inhibitor, baricitinib or OLUMIANT as a first-in-class systemic treatment for adults suffering from alopecia. The medication comes in 1,2 and 4 mg tablets and the study leading to approval showed that patients responded best to the 4 mg daily tablet over 36 weeks. Patients could be in the study if they had 50% or greater loss of scalp hair loss and with the 4 mg dose were able to achieve 80% scalp coverage compared to baseline. About a quarter of those patients were able to achieve 90% scalp hair coverage which seems to be nearly miraculous. Eyebrows and eyelashes also showed significant improvements over 36 weeks.
Who is a good candidate for OLUMIANT?
Someone who has been diagnosed with alopecia and is in reasonably good health and has tried and failed traditional therapies. Side effects can be serious including serious infections, cancer, cardiovascular event, clots and even death. In the study, however, the side effects were mild and included upper respiratory tract infection, elevated liver enzymes, high cholesterol, acne, headache, urinary tract infections, abdominal pain, shingles and weight gain.
More than 2.5 million Americans suffer from alopecia. Hair loss can feel like a loss of identity to some people. Many with alopecia withdraw from activities, friends and family. Loss of hair in the eyes, nose, and ears can even affect hearing, allergies, and cause eye irritation. If you or someone you know suffers from alopecia, call Toyos Clinic Hair Restoration at 901.800.6638 for a free consult to decide if OLUMIANT is right for you.
For more information, visit Dr. Brian A. Levine's social media: